VIRTUAL PRODUCTION
BUILDING BRANDS FOR A NEW BREED OF CONSUMERS
What is virtual production?
Virtual production is a method of film and video game production that utilizes real-time technology such as game engines and augmented reality to create computer-generated sets and environments. It allows filmmakers and game developers to plan, shoot and even post-produce their projects entirely in digital space, reducing the need for physical sets and location shoots, saving time and money. It also allows greater creative freedom and flexibility in the filmmaking process. Virtual production can be used for pre-visualization, animation, and visual effects, and it can be used for live-action filming as well. With advancements in technology, virtual production is becoming more accessible to independent filmmakers and small studios.
Virtual production allows for cost-effective, efficient film and video game production.
Virtual production is a revolutionary method of film and video game production that utilizes real-time technology such as game engines and virtual reality to create virtual sets and environments. It allows filmmakers and game developers to plan, shoot and even post-produce their projects entirely in a virtual space. This eliminates the need for physical sets and location shoots, which can be both time-consuming and costly. By using virtual production, filmmakers and game developers can save money on set construction and location fees, making the production process more cost-effective and efficient. Additionally, virtual production provides greater creative freedom and flexibility in the filmmaking process, allowing for more precise pre-visualization, animation, and visual effects. With the advancements in technology, virtual production is becoming more accessible to independent filmmakers and smaller studios, making it a great alternative to traditional production methods.
Virtual production can be used for pre-visualization, allowing directors and cinematographers to plan shots and visual effects before filming.
A virtual production is a powerful tool for pre-visualization, allowing directors and cinematographers to plan shots and visual effects before filming. This is done by creating virtual sets and environments that can be explored and manipulated in real time. This allows filmmakers to try out different camera angles, lighting setups, and visual effects, before committing to a final shot. This can save time and money on set by reducing the need for multiple takes and reshoots and allows for more precise planning and execution of shots. Additionally, virtual pre-visualization can also be used to create storyboards, animatics, and technical pre-vis, which can be used to communicate the visual language of the project to the rest of the crew, and stakeholders. With virtual production, filmmakers and game developers can experiment and iterate on their creative vision until they find the perfect shot.
With the advancements in technology, virtual production is becoming more accessible to independent filmmakers and smaller studios.
As technology continues to advance, virtual production is becoming more accessible to independent filmmakers and smaller studios. This is due to the availability of more affordable and user-friendly virtual production software, hardware, and tools. In the past, virtual production was primarily used by large studios with big budgets, but now, with the advancements in technology, it is becoming more accessible to a wider range of filmmakers and game developers. Many game engines and virtual reality platforms are now being adapted for use in virtual production, making it easier for independent filmmakers and smaller studios to create high-quality virtual sets and environments. Additionally, there are also more affordable virtual production hardware options available, such as motion capture suits, virtual cameras, and LED walls, which allow independent filmmakers and smaller studios to create virtual production setups with a limited budget. With the increasing accessibility of virtual production, it is becoming a more viable option for independent filmmakers and smaller studios to create high-quality films and video games at a fraction of the cost of traditional production methods.
Virtual production software
Virtual production software refers to the various tools and programs that are used to create and manipulate virtual sets and environments. These tools can be used for pre-visualization, animation, and visual effects, as well as live-action filming. Some examples of virtual production software include:
Game engines such as Unity and Unreal Engine, are commonly used to create virtual sets and environments for film and video game production.
Motion capture software such as MotionBuilder and Vicon is used to capture and record live-action movement and apply it to virtual characters.
Virtual camera software such as the virtual camera in Unreal Engine, allows the director to move and operate a virtual camera in real time.
3D modeling and animation software such as Autodesk Maya, Blender, and Houdini, is used to create and manipulate 3D assets for use in virtual production.
Virtual reality software such as the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive can be used to explore and interact with virtual sets and environments in real time.
LED wall software such as Notch allows you to create and control real-time visual effects, animations, and video content on LED walls.
These are just a few examples of virtual production software, and there are many other options available depending on the specific needs of the production.
Virtual production hardware
Virtual production hardware refers to the various devices and equipment that are used to create and capture digital sets and environments. Some examples of virtual production hardware include:
Motion capture suits: These are worn by actors to capture their movements and apply them to virtual characters.
Virtual cameras: These are cameras that are controlled in real-time, allowing the director to move and operate a virtual camera in the virtual set environment.
LED walls: These are large displays that can be used to create virtual environments or to project live-action footage as background plates in real time.
Virtual reality headsets: These are worn by the director, allowing them to explore and interact with the virtual set in real time.
Tracking systems: These are used to track the movement of cameras, actors, and other objects in real time in virtual space.
Control panels and input devices: These are used to control the virtual cameras, lights, and other elements of the virtual environment in real time.
High-end workstations: These are powerful machines that can run virtual production software and hardware.
These are just a few examples of virtual production hardware, and there are many other options available depending on the specific needs of the production. Some of the hardware can be quite expensive, but as technology develops, it is becoming more accessible and affordable for independent filmmakers and small studios.
latest cases
CRYPTO CROOK
FINANCIAL STABILITY
ASTON MARTIN ME
2022 CAMPAIGN
KANYE WEST
HEAVEN AND HELL 2D CEL ANIMATION
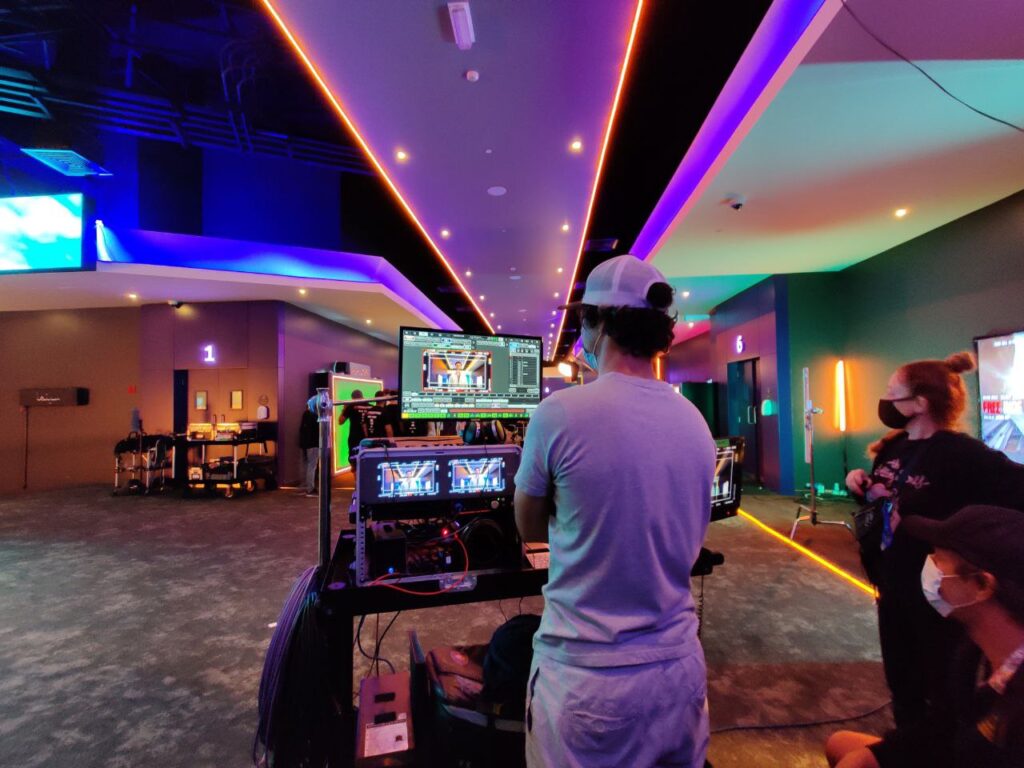






get trendy with us
We recently celebrated 8 years of our company, bringing the best in visual effects and content production services to the rapidly growing commercial film, series, and video production market. Since its founding in Dubai, JJ has produced countless animated films, commercials including some of the awaring winning project.


Brand
Collaboration






































PARTNERS
in Crime